The modern real estate investment trust (REIT) era began in the early 1990s, and their initial appeal was quite simply as a means of participating in the benefits of ownership of commercial real estate without the pitfalls of illiquidity and weaker disclosure. The asset class has matured over the last 30 years into what many may regard today as the benchmark for quality, capital stewardship, transparency, and governance within the overall real estate landscape. Lessons learned from challenges gone by have certainly played a role in the evolution of the REITs sector over the past three decades. For example, the global financial crisis (GFC) of 2008/2009 altered the way many listed REITs operated with respect to financial leverage (debt); today many REITs operate with debt ratios at historic lows. The more recent COVID-19 pandemic introduced an unprecedented set of challenges, but in the aftermath, many listed REITs improved their internal practices and disclosure.
Another outcome has been rapid technological and behavioral change affecting how people live, work and play, with massive implications for utilization of retail and office space. In turn, the underlying composition of the REIT sector has shifted away from those traditional uses toward categories such as industrial, residential, self-storage, health care, data centers and cellular towers, each with strong secular underpinnings.
We believe this bodes well in the age of heightened uncertainty that engulfs the world we live in. Here we focus on four characteristics that pertain to the REIT sector and that can provide much-needed visibility amid these turbulent times: (1) reliable revenues, (2) compositional change, (3) top-tier transparency, and (4) financial flexibility.
Reliable revenues
REITs derive the majority of their revenue as rental income from tenants who sign leases on the space the REIT owns. While there are exceptions such as lodging, self-storage and residential, these leases are largely multi-year contracts, thereby providing for good visibility of top-line income. The portfolios themselves tend to be highly occupied, and the consistency of this metric over time evidences the quality proposition for the REIT sector as a whole. Importantly, even in the severest of downtowns, e.g., the GFC, same-store net operating income (NOI) growth for the US REITs was modestly negative for just a few quarters before recovering strongly in subsequent years, underpinned by solid rent growth as well as high occupancy (See Exhibit 1).
Exhibit 1: Same Store Quarterly NOI Growth (right click to enlarge)
Compositional change
One of the big themes in REITs over the past decade or so has been the significant shift in underlying asset composition. Specifically, we have seen large reductions in the representation of retail and office exposure, increases in more fundamentally supported segments, such as industrial and apartments, as well as an expansion into alternative categories including towers, data centers, manufactured homes, single-family rentals and senior housing. We believe this has reduced cyclicality in the sector as demand increasingly becomes more influenced by secular trends such as the growth of e-commerce and aging populations.
In addition, we would highlight two further benefits: (1) an increasing number of property types with contrasting economic sensitivities facilitates greater diversification and increases the potential for higher risk-adjusted returns, and (2) wide performance dispersion among categories can create more opportunities for experienced REIT investment professionals.
Top-tier transparency
Like other publicly registered companies, REITs must disclose financial information to investors and report on material business developments and risks on a timely basis, as governed by the US Securities and Exchange Commission. REITs also provide an additional level of transparency due to a legislative requirement for REITs to pay out most of their income to shareholders as dividends, leading them to engage more frequently with capital markets as they look to execute on their growth strategies. Consequently, REIT management teams need to open their playbooks to investors, explaining their plans and justifying their use of investors’ money. All of these factors provide REIT investment professionals with enhanced visibility into REITs’ finances and operations. In addition to what is statutorily required, investors today can also expect to receive detailed information with respect to operating metrics, leasing activity, development projects, transaction activity and debt schedules, to name just a few.
Financial flexibility
Access to permanent capital afforded by the public equity and debt markets is a significant advantage to REITs, in our view, especially in tougher economic settings. A key characteristic of the sector is that most constituents have investment-grade credit ratings, for instance as of August 31, 2023, 72 US equity REITs had an investment-grade credit rating with S&P, Moody’s or Fitch.1
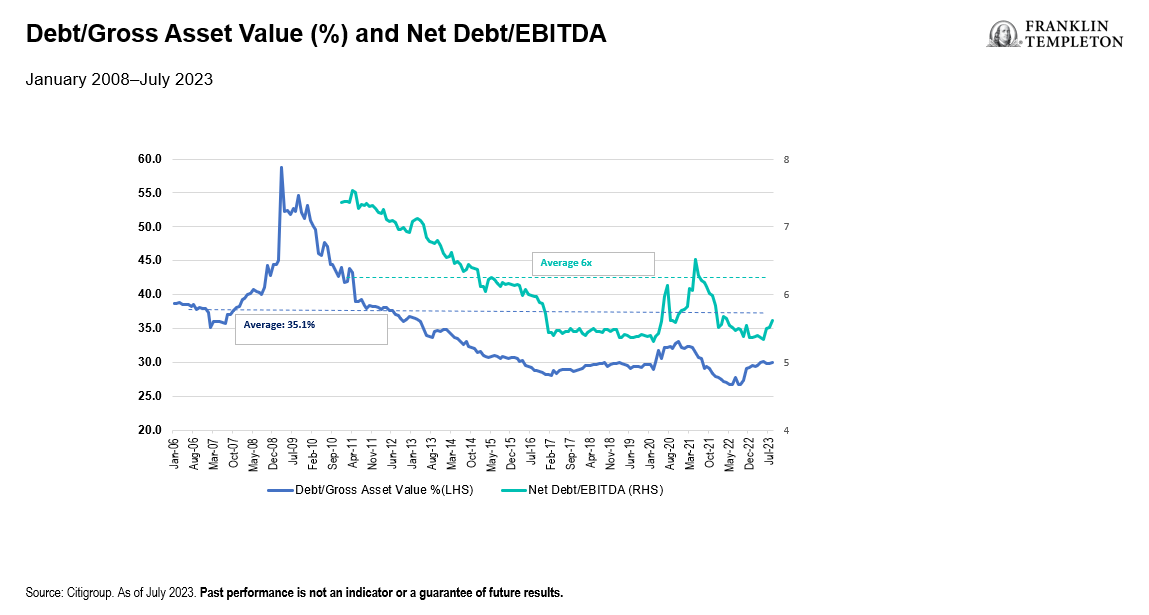
Additionally, after an extended period of capital discipline (dating back to the GFC), the REIT sector today operates at historic low levels of leverage with net debt to EBITDA of around 5.5x.2 This is an enviable position in the event of a tighter capital environment, not to mention the ability to take advantage of distressed opportunities when they arise.3 With healthy balance sheets, long-term and largely fixed financing in place, and a solid organic story (supported by largely secular tailwinds), we believe REITs are well placed to grow earnings and dividends in the coming years.
Exhibit 2: Debt/Gross Asset Value(%) and Net Debt/EBITDA (right click to enlarge)
Value in uncertain times
These characteristics among others underpin the sector’s solid positioning, particularly when we consider the uncertain financial landscape that reigns. In today’s environment, there is a lot going on. From the cost of living, shifts in interest rates, the possibility of a recession and banking system fears, to climate change, wars, US elections, the impact of artificial intelligence and the ever-evolving labor market—it’s enough to make anyone’s head spin. During times like these, an investor may consider an allocation to listed REITs, an asset class which has historically proven to be a reliable and profitable investment.
One might infer that REITs, with their list of attractive attributes, ought to possess a cash flow multiple that is competitive versus that of other asset classes. Indeed, this has regularly been the case over their history, except for periods like we find ourselves more recently (i.e., rapid increases in interest rates).
As of September 30, 2023, the FTSE NAREIT All Equity REIT Index was 25% below its peak established on December 31, 2021.4 Broader equities, as represented by the S&P 500, were 4% below their peak as of September 30, 2023, by comparison.5 The REIT sector today trades at a significant discount to estimated net asset value as well as to non-traded vehicle pricing, an implied cap rate averaging above 6%, and a funds from operations multiple that is two turns below that of the S&P 500 Index price-to-earnings average.6
In summary, we believe this is an opportune time to gain access to REITs, which can provide a high level of visibility in this era of heightened uncertainty.
WHAT ARE THE RISKS?
All investments involve risks, including possible loss of principal. Equity securities are subject to price fluctuation and possible loss of principal. Fixed income securities involve interest rate, credit, inflation and reinvestment risks, and possible loss of principal. As interest rates rise, the value of fixed income securities falls.
Alternative strategies may be exposed to potentially significant fluctuations in value.
Real estate investment trusts (REITs) are closely linked to the performance of the real estate markets. REITs are subject to illiquidity, credit and interest-rate risks, and risks associated with small- and mid-cap investments.
Privately held companies present certain challenges and involve incremental risks as opposed to investments in public companies, such as dealing with the lack of available information about these companies as well as their general lack of liquidity.
Active management does not ensure gains or protect against market declines.
IMPORTANT LEGAL INFORMATION
This material is intended to be of general interest only and should not be construed as individual investment advice or a recommendation or solicitation to buy, sell or hold any security or to adopt any investment strategy. It does not constitute legal or tax advice. This material may not be reproduced, distributed or published without prior written permission from Franklin Templeton.
The views expressed are those of the investment manager and the comments, opinions and analyses are rendered as at publication date and may change without notice. The underlying assumptions and these views are subject to change based on market and other conditions and may differ from other portfolio managers or of the firm as a whole. The information provided in this material is not intended as a complete analysis of every material fact regarding any country, region or market. There is no assurance that any prediction, projection or forecast on the economy, stock market, bond market or the economic trends of the markets will be realized. The value of investments and the income from them can go down as well as up and you may not get back the full amount that you invested. Past performance is not necessarily indicative nor a guarantee of future performance. All investments involve risks, including possible loss of principal.
Any research and analysis contained in this material has been procured by Franklin Templeton for its own purposes and may be acted upon in that connection and, as such, is provided to you incidentally. Data from third party sources may have been used in the preparation of this material and Franklin Templeton (“FT”) has not independently verified, validated or audited such data. Although information has been obtained from sources that Franklin Templeton believes to be reliable, no guarantee can be given as to its accuracy and such information may be incomplete or condensed and may be subject to change at any time without notice. The mention of any individual securities should neither constitute nor be construed as a recommendation to purchase, hold or sell any securities, and the information provided regarding such individual securities (if any) is not a sufficient basis upon which to make an investment decision. FT accepts no liability whatsoever for any loss arising from use of this information and reliance upon the comments, opinions and analyses in the material is at the sole discretion of the user.
Products, services and information may not be available in all jurisdictions and are offered outside the U.S. by other FT affiliates and/or their distributors as local laws and regulation permits. Please consult your own financial professional or Franklin Templeton institutional contact for further information on availability of products and services in your jurisdiction.
________
1. Source: Bloomberg. EBITA = earnings before taxes, interest and amortization.
2. Source: Citigroup. As of July 2023.
3. Source: Citigroup. As of September 30, 2023.
4. Source: Bloomberg. The FTSE Nareit All Equity REITs Index is a free-float adjusted, market capitalization-weighted index of US equity REITs. Constituents of the index include all tax-qualified REITs with more than 50 percent of total assets in qualifying real estate assets other than mortgages secured by real property. Indexes are unmanaged and one cannot directly invest in them. They do not include fees, expenses or sales charges. Past performance is not an indicator or a guarantee of future results.
5. Source: Bloomberg.
6. Source: Citigroup. January 2006 through September 30, 2023.