Remember the adage, “don’t fight the Fed?” It was a key tenet of financial markets’ folk wisdom for so long, passed on from the more experienced traders to the younger ones; a mantra repeated in countless media interviews. If the Federal Reserve (Fed) signaled it would do one thing and you bet against it, the wisdom was, you would lose money.
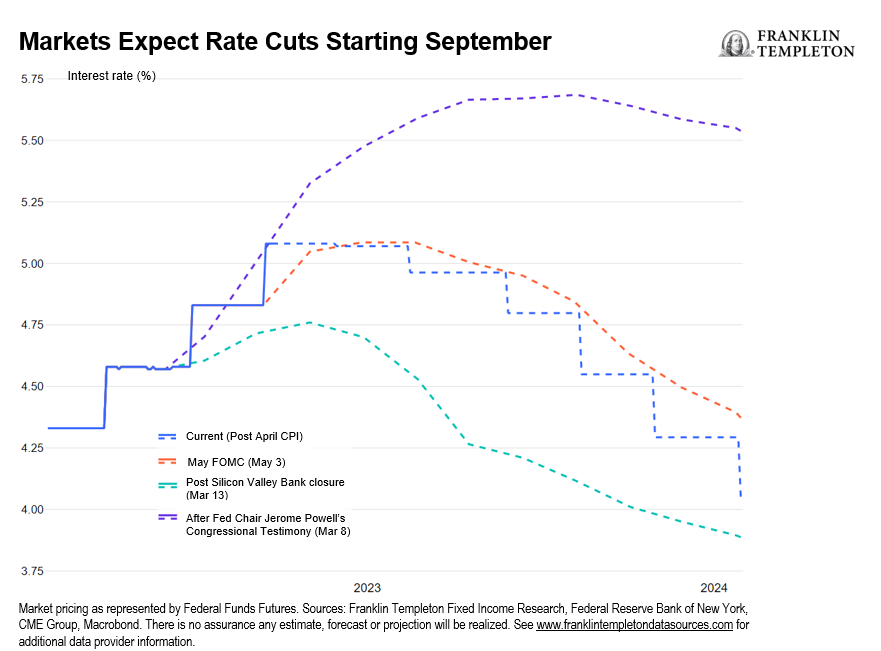
It now seems as though that wisdom no longer applies. It was unquestionable when the Fed signaled commitment to loose monetary policy. But now that the central bank signals an intention to keep policy tight for quite a while, most investors are quite happy to bet against it. Markets are currently pricing in significant interest rate cuts—more than one percentage point between now and January of next year. US Treasuries have again rallied even in response to an April Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation report that shows headline and core measures broadly stable at about 5% and 5.5% respectively (4.9% on the headline, to be precise).
Throughout this tightening cycle, markets have more often than not been fighting the Fed, whether by forecasting a lower peak rate, an earlier pivot to loose policy, or deep rate cuts. Are the markets right?
This tug of war between markets and the Fed also reflects the very elevated uncertainty that we at Franklin Templeton Fixed Income had been warning about for some time—uncertainty on both the macroeconomic environment and the policy response.
I see three key elements of uncertainty that will eventually determine whether investors have picked the wrong fight.
First: The growth outlook. Betting on significant rate cuts between now and early next year makes sense if you expect the economy to buckle into a very sharp recession. I continue to regard this as an unlikely outcome. Yes, the economy has been hit by sustained headwinds: higher interest rates, the inflation-driven erosion of purchasing power and most recently, banking-sector turmoil.
But overall, the US economy insists on demonstrating impressive resilience. Household consumption in particular remains robust; the labor market goes from strength to strength, with the unemployment rate in April at 3.4%, which tied with January as being the lowest since May 1969.1 And, the employment rate for people of prime working age (25-54 years old) is close to the highest levels on record. As far as the outlook for corporate America is concerned, neither equity markets nor corporate credit spreads seem to anticipate a meltdown. The recent banking turmoil has clearly raised the risk of a more meaningful credit tightening that could impact growth, and this risk should not be dismissed; however, at this stage the clearest danger sign is a significant decline in regional banks stocks. While concerning, this does not by itself foreshadow a broad credit crunch; indeed, the Senior Loan Officers Opinion Survey still only shows an incremental tightening in lending standards. A deep recession would justify a rapid turnaround by the Fed—but it does not appear likely, nor does it seem to be what risk markets expect.
Second: Inflation and the real interest rate. Suppose that inflation declines faster than expected. This might justify a pivot, but inflation would have to come down far and fast to allow for the kind of rate cuts the market is pricing in. In the March economic projections, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) saw core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) between 3.5% -3.9% by the end of this year and projected a corresponding fed funds rate above 5% (5.1%-5.6%), near its current 5.00%-5.25% level.
The last reading on core PCE (March) was 4.6%. Even allowing for a somewhat looser stance on the back of the banking turmoil, core PCE would need to fall sharply and quickly below 3% for the Fed to feel comfortable cutting rates by over one percentage point. Again, not impossible, but unlikely, in my view. The just-released April CPI report confirms that the pace of disinflation remains excruciatingly slow: Both headline and core measures rose 0.4% month-on-month, and both edged lower by a mere 0.1%, to 4.9% and 5.5% respectively.
Core services inflation ex-housing showed a more meaningful drop, as cooling prices in categories like hotels, airfares, eating out and household furnishings showed consumers might be beginning to pull back a bit. But it is just one data point, and on the other hand, core goods prices keep ticking up. At this pace it’s a long, long way back to 2%. Note also that with these numbers, the policy interest rate is barely above headline inflation. Yes, the real interest rate should be computed using expected inflation, which is lower, but previous successful disinflations have all required getting the policy interest rate above contemporaneous inflation, and we have barely just gotten there. Again, this suggests the Fed should be in no hurry to lower rates even as disinflation slowly moves ahead.
The third element of uncertainty pertains to the Fed’s anti-inflation stamina. Over the past decade and a half, the Fed has reliably defaulted to a very dovish stance; this might lead investors to believe that once the inflation emergency has receded, the Fed will again err on the side of dovishness to minimize risks to growth and to asset prices. The Fed’s own communication during this hiking cycle has at times given reason to think this might indeed be the case.
Times have changed, however. The inflation scare has already proved more serious and persistent than the Fed initially anticipated, and the recent banking sector turmoil stands as a sober reminder of the risks to financial stability that can build up as a consequence of overly loose monetary policy. Overall, there is much broader acceptance of the common-sense idea that even as inflation comes back to target, monetary policy should not revert to the emergency setting of the post-global financial crisis and pandemic period.
Bottom line: As some of the macro uncertainty dissipates, I think we will get further evidence that the economy is gradually heading for a minor recession, not a deep one, and that progress in disinflation will remain painfully slow. If that’s the case, financial markets may discover that they’ve picked the wrong fight, and should have listened to their own old wisdom: Never fight the Fed.
WHAT ARE THE RISKS?
All investments involve risks, including possible loss of principal. The value of investments can go down as well as up, and investors may not get back the full amount invested. Bond prices generally move in the opposite direction of interest rates. Thus, as prices of bonds in an investment portfolio adjust to a rise in interest rates, the portfolio’s value may decline. Changes in the credit rating of a bond, or in the credit rating or financial strength of a bond’s issuer, insurer or guarantor, may affect the bond’s value.
IMPORTANT LEGAL INFORMATION
This material is intended to be of general interest only and should not be construed as individual investment advice or a recommendation or solicitation to buy, sell or hold any security or to adopt any investment strategy. It does not constitute legal or tax advice.
The views expressed are those of the investment manager and the comments, opinions and analyses are rendered as at publication date and may change without notice. The information provided in this material is not intended as a complete analysis of every material fact regarding any country, region or market. All investments involve risks, including possible loss of principal.
Data from third party sources may have been used in the preparation of this material and Franklin Templeton (“FT”) has not independently verified, validated or audited such data. FT accepts no liability whatsoever for any loss arising from use of this information and reliance upon the comments, opinions and analyses in the material is at the sole discretion of the user.
Products, services and information may not be available in all jurisdictions and are offered outside the U.S. by other FT affiliates and/or their distributors as local laws and regulation permits. Please consult your own financial professional or Franklin Templeton institutional contact for further information on availability of products and services in your jurisdiction.
Issued in the U.S. by Franklin Distributors, LLC, One Franklin Parkway, San Mateo, California 94403-1906, (800) DIAL BEN/342-5236, franklintempleton.com – Franklin Distributors, LLC is the principal distributor of Franklin Templeton U.S. registered products, which are not FDIC insured; may lose value; and are not bank guaranteed and are available only in jurisdictions where an offer or solicitation of such products is permitted under applicable laws and regulation.
______
1.Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics. April unemployment rate as of May 5, 2023.